GIMAT Products and their Applications at a Glance
As a complete provider of water and wastewater measurement technology, we offer you a comprehensive range of standard devices for online measurement and online analysis for all relevant online parameters and application areas. Our portfolio is supplemented by automatic sampling devices, hand-held devices and laboratory equipment.
The special strength of GIMAT lies in the fact that, in addition to standard devices, it is also possible to supply customized systems for online measurements according to your specific specifications.
GIMAT Product Range
Applications
Investments in process analytics pay for themselves particularly quickly. With good control, a plant can keep product losses low and deliver products of the same high quality over the long term. The prerequisite for this is that accurate and meaningful data is available.
The main fields of application of our on-line measuring instruments and laboratory measuring systems include: refineries, food & beverage industry, pulp and paper and the chemical industry. The applications include the determination of arsenic in drinking water, the Brix value of cooling lubricants, the viscosity measurement of oils and the determination of the sugar content in soft drinks.
Accurate Dosage Saves Money
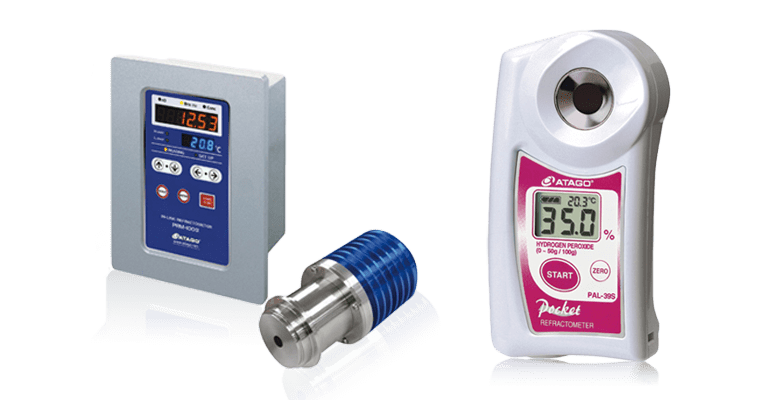
In many applications, refractometers now take over the concentration monitoring of critical process liquids. For example, the physical or chemical surface treatment of materials is often carried out for aesthetic purposes, for curing or for improving the corrosion resistance. Treatment techniques include cleaning, polishing, etching and coating. For the surface treatment to achieve the desired, best possible result, the applied agent must have the optimum concentration. Otherwise, the texture of the surface may suffer significantly. If, for example, beverage can receive poor surface treatment, no dye adheres to the surface. The container is then rendered unusable. It is therefore essential to monitor the concentration of solutions. Continuously measuring in-line refractometers can be used to automate the correct dosage of the substance.
Ensure the Degree of Purity
The electrical conductivity is a measure of the ion concentration of a measuring solution. The more salts, acids or bases are dissociated in the measuring solution, the higher is their conductivity. Water contains predominantly ions of dissolved salts. The conductivity thus provides a measure of the purity of water. In industrial production processes, conductivity measurement is used e. g. for process control.
Reduce Waste Water Costs
Municipal drainage systems often provide heavy-pollutant surcharges for industrial and commercial wastewater from indirect discharges. In one state of Germany, Bavaria, for example, a rate of 150% of the cubic meter price will be charged for industrial and commercial sewage water, which causes higher cleaning costs than household wastewater (more than 30% higher). The parameter most frequently used for the determination of heavy pollutant surcharges is the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD). It is therefore recommended for indirect discharges to determine the COD in addition to the continuous detection of the waste water quantity. This can be done by time or flow proportional sampling with automatic sampling devices and subsequent lab determination of the COD, or with the help of continuously operating probes or analyzers. Instead of paying a fee based on estimated (and often too high) COD values, a company can prove the actual annual load and achieve significant cost reductions by using measurement equipment.
Neutralization and Detoxification
The continuous measurement of the pH is of great practical importance. The acidic or alkaline character of the medium plays a key role in many chemical, biological, mechanical and physical processes. Numerous reactions, such as precipitation or detoxification, only proceed when the pH is suitably adjusted. In the field of wastewater treatment, the following harmful effects can occur under extreme pH conditions:
- The microorganisms for biological wastewater treatment are sensitive to bases and acids; the pH should be in the neutral range around pH 7.
- pH values of 6.5 or lower lead to the gradual destruction of metallic materials and construction parts and damage the sewer system.
- The solubility of many substances changes as a function of pH and temperature. Undesired precipitation may result. Legal regulations often restrict sewage discharges into the public sewer network to a pH range between 6.5 and 9.5. For many companies which discharge their wastewater into public sewer systems it may therefore be necessary to carry out pretreatment of the waste water in a neutralization plant.
Keep Salt Below Limit
The electrical conductivity is a measure of the ion concentration of a solution. The more salts, acids or bases are dissociated in the measuring solution, the higher its conductivity. Wastewater contains ions of dissolved salts. The conductivity thus provides a statement about the salt load in the waste water.
Our devices are suitable for the monitoring of wastewater in all stages of wastewater treatment.
- Inlet
- mechanical pre-treatment
- Biology / aeration tank
- return sludge
- Discharge
- Sludge Digester
We supply a large number of online measuring systems as well as automatic sampling devices for all measurements required for self-monitoring.
Proof of Carbon Reduction
An important task of a sewage treatmet plant is to reduce the organic load of the sewage in addition to nitrogen and phosphate elimination. The organic compounds consist primarily of the elements carbon and hydrogen. In the course of the cleaning process, they are ultimately converted into carbon dioxide and water using oxygen. In order to describe the organic load, the sum parameters TOC, DOC, COD and / or BOD are used.
Nitrogen Elimination
Especially in the case of biological wastewater treatment, the precise and continuous monitoring of the oxygen content is a condition for optimum and trouble-free operation of the plant. The efficiency and the energy costs of the biological purification process, both in the nitrification and denitrification stages, are essentially determined by the quality of the aeration control. Supported by our measuring technology, you can achieve a load-oriented regulation of the oxygen input. The activity of microorganisms in nitrification increases with increasing O2 concentration. At about 2 mg / l dissolved oxygen (DO) however, an economic limit is reached, since further increase in the oxygen content no longer causes substantial acceleration of the process, but requires much more energy for the blowers. A concentration-dependent control of the aeration system can therefore save a considerable amount of energy, since the power consumption of the aeration system represents the greatest operating cost factor of a biological sewage treatment plant. Residual oxygen on the other hand negatively affects the denitrification. For this reason a minimal concentration of O2 is desired denitrification (anaerobic / anoxic conditions). In nitrification however, the oxygen concentration should precisely meets the needs of the microbiology in the aeration tank. Only the use of a precise and reliable measuring system ensures an efficient and thus energy-saving regulation of this process.
Further Reduction of Energy Costs
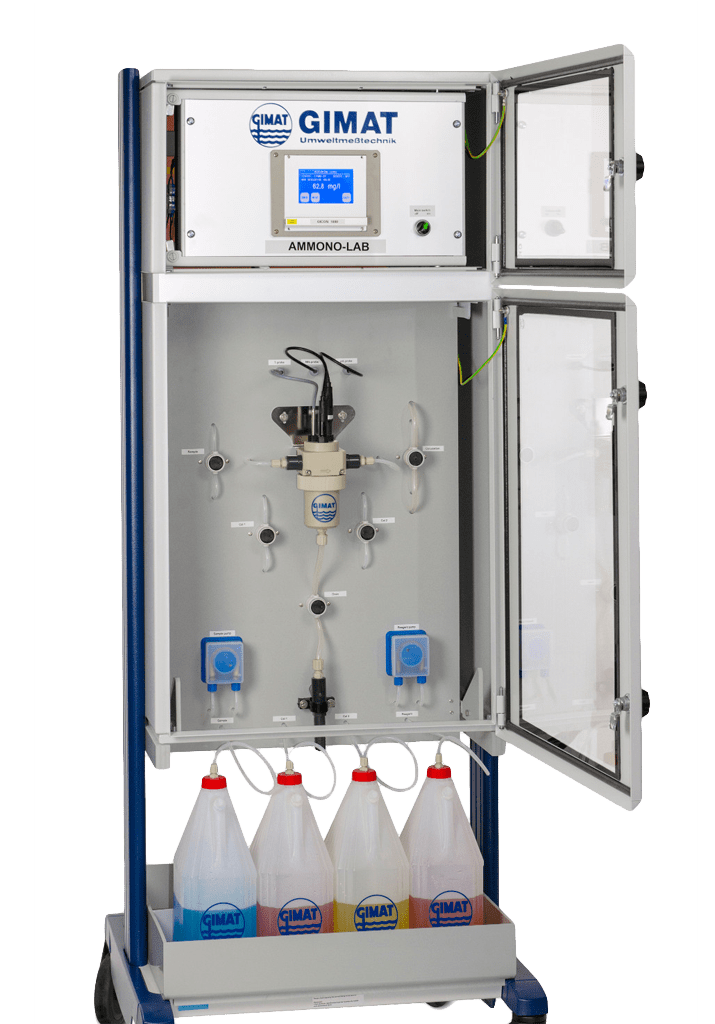
In modern sewage treatment plants the parameters ammonium and nitrate are determined in addition to oxygen, as they are relevant for the nitrification and denitrification.
In order to minimize the energy consumption in the aeration tank, a complete nitrogen oxidation is to be achieved with efficient and low DO concentration. Optimal growth of the nitrifiers usually requires higher concentrations of dissolved oxygen than the degradation of organic C compounds. Aeration based on the online measurement of ammonium (NH4-N) makes the nitrification process transparent and offers much higher potential for energy savings than in a pure DO control mode. Bulking sludge is prevented in the lower operating range and the oxygen input is limited in the case of disturbances of the NH4 digestion (e. g. due to a disturbed nutrient ratio of carbon: nitrogen: phosphate). As a result, considerable potential savings can be achieved.
Further Improvements to Nitrification, Denitrification and Biological P-elimination
In order to achieve a sufficient degree of nitrification, a certain sludge age must not be exceeded in the long term. This is determined by the excess sludge flow and the dry substance content in the quenching basin.
It can be measured with a mixed liquor suspended solid probe. The denitrification (N elimination) and, in some cases, the biological P-elimination are also significantly improved, the greater the suspended solids content is.
Optimization of Chemical Phosphate Precipitation
In order to comply with the P-limit values, a chemical-physical phosphate elimination with metal salts (usually Fe3+ or Al3+) is often required in the sewage treatment plant. The precipitation process can be controlled or regulated very effectively via the use of orthophosphate analyzers. Especially large plants achieve significant savings in precipitant consumption.
Removal of Micropollutants
The introduction of a fourth treatment step for the removal of trace substances such as pharmaceuticals or microplastics from sewage has gained more and more attention in the last few years. The number of experts who expect regulations in this field in the next few years is growing steadily. Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent and is therefore ideally suited for the treatment of these impurities, which pass through the previously established treatment stages unchanged. The ozone generators and the contact containers for the reaction are technically sophisticated and can be handled safely. The reaction time is typically 10-30 min. Thus, the ozonisation is a promising, efficient process for the 4th purification stage. In order to ensure that the concentration of ozone meets the requirements, an online measurement is essential.
The monitoring of surface water allows conclusions regarding the development of the water quality and industrial discharges. The monitoring of the water quality can also be of interest where the impacts of shipping on the ecosystem are to be investigated.
Measured variables for water monitoring can be:
- Dissolved oxygen content for estimation of eutrophication
- temperature
- pH value
- conductivity
- Redox potential as an indicator of the biological self-purification capacity of the water body
- turbidity
- ammonium
- nitrate
- ortho / total phosphate
- Heavy metal content
- Carbon content expressed by one of the sum parameters COD, Spectral Absorption Coefficient (SAC) or TOC.
When operating a landfill, official regulations usually include the requirement to capture a range of parameters. These include, among others
- Water quality
- Quantity of surface drains
- Quantity of leachate water as well as level and possibly water quality measurements in nearby waters
The flow measurement serves to explain the effectiveness of the surface seals and the landfill behavior. Since a reduction in the amount of seepage water is to be expected over the years, a measuring method is required which also measures very small flow quantities accurately. A data logger is useful to record the development of the amount of leachate water over time.
The quality of the pool water is subject to national and international standards and regulations, which reflect high hygiene standards and ensure the health of the bathers. In order to meet these requirements, reliable measurement, regulation and dosing technology are needed. This guarantees hygienic conditions and high water quality.
Maximum Hygiene and Highly Economic
We offer tailor-made solutions for public (pH, chlorine) or privately operated swimming pools, for example in wellness hotels (pH, redox, chlorine). A pH-redox system can be designed in a variety of ways, from a simple and cost-effective system to complex solutions, with high operating comfort in the upper price segment. In addition to pH control, the chlorine concentration is controlled indirectly via a redox electrode. Both system types are user-friendly, reliable and suitable to meet the requirements, so that the hygiene and health of the guests are ensured.
All our measuring instruments and online analyzers are also suitable for use in drinking water monitoring. Be it in the public drinking water supply or in the beverage industry. Regulations often require monitoring of a number of parameters in drinking water treatment. Similar procedure apply to the food industry where drinking water is used, e.g. in the production of soft drinks. The risk of lost batches can thus be avoided.
Main parameters
- temperature
- pH value
- turbidity
- conductivity
- coloring
- chlorine / chlorine dioxide
- ozone
- dissolved oxygen
- nitrate
- ORP
- UV absorption
- level
- Pressure / Differential Pressure
- Flow, velocity
The safety concepts for cooling water in the chemical industry stipulate that, under certain conditions, the cooling water must be monitored automatically. Only if leakages, e. g. in heat exchangers are detected, immediate countermeasures can be taken. For this purpose we offer appropriate inline- and online-measuring instruments and analyzers for the all relevant parameters.
- pH value
- conductivity
- ORP
- turbidity
- refractometry
- photometry
- Oil detectors
- Mercury Monitors
- TC (total carbon, total carbon)
- TOC (Total Organic Carbon: total organic carbon)
- DOC (Dissolved Organic Carbon (dissolved organic carbon)